Operations management is the power to act, according to Harvard Business School Professor Marco Lansiti, head of the university’s Technology and Operations Management Unit. It involves creating, capturing, and sharing value for customers, shareholders, and the entire business ecosystem. In today’s unpredictable and volatile business environment, effective operations management is essential for success.
Table of Contents
- What Is Operations Management?
- Key Functions of Operations Management in an Organization
- Essential Skills You Need to Succeed as an Operations Manager
- How SweetProcess Can Make Your Job Easier as an Operations Manager
- Types of Operations Management
- Major Performance Objectives of Operations Management
- Frameworks for Analyzing Operations Management
- Challenges of Operations Management (And How to Overcome Them)
- Factors Influencing the Performance of Operations Management
- Manage Your Business Operations Effectively Using SweetProcess
What is Operations Management?
Operations management (OM) is all about delivering the power to act by linking process and value. It involves planning, organizing, and supervising manufacturing and production processes to create shareholder value and satisfy customer demands. Operations managers make strategic and tactical decisions to optimize efficiency and resource utilization. They play a crucial role in the delivery of products and services to the market.
Why Is Operations Management Important?
Enhances Team Collaboration

Effective operations management facilitates team collaboration and boosts productivity. Take the example of Nestlé, which has over 350 factories worldwide. By equipping operators with iPads, Nestlé ensures seamless collaboration and process visibility. Operators use their iPads as dashboards, tracking progress, checking task status, and addressing bottlenecks in real-time. Tools like business process management enhance collaboration and streamline operations.
Helps Achieve Business Objectives
To achieve business objectives, operations management plays a crucial role. It aligns strategic goals with production capacity, supply chains, and logistics. By optimizing processes, operations managers lower costs, enhance quality control, and improve customer satisfaction. Nestlé’s focus on operations management has resulted in increased profits and market share.
Boosts Employee Productivity
Employee productivity is a significant challenge for operations managers. Business process platforms can engage employees, facilitate learning, and enhance task performance. Clear task assignments, streamlined workflows, and skill-building initiatives enable operators to work efficiently. For instance, Nestlé fosters a culture of honesty and transparency by providing ongoing training and upskilling opportunities.
Improves Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a key driver of business success. Operations management plays a crucial role in enhancing customer satisfaction by resolving challenges efficiently. First call resolution (FCR) is a critical metric in assessing customer satisfaction. Operations management tools like knowledge base features and automation can improve FCR rates and ensure timely, consistent product delivery.
Reduces Costs
Cost reduction is a primary objective for businesses. Operations management teams leverage technology to lower costs and optimize resource allocation. Digital technology helps eliminate non-value-added activities, streamline processes, and increase efficiency. It also reduces overhead costs, improves time to market, and maximizes profitability.
Ensures Product Quality
Operations management enhances product quality by implementing high-quality control systems and monitoring production processes. By rectifying any defects and providing standard operating procedures, operations managers ensure consistency and adherence to regulations. Training and feedback loops improve employee knowledge and enhance product quality.
Increases Revenue
Agile and adaptable businesses with effective operations management enjoy higher productivity and timely product delivery. This, in turn, drives customer satisfaction, higher sales, and increased revenue. Nestlé’s focus on operations digitization has resulted in consistent operating profit margins and earnings-to-share margins.
Key Functions of Operations Management in an Organization
Strategic Alignment
Strategic alignment ensures that the operations management team aligns organizational objectives with its core goals. By translating goals into actionable plans, operations managers allocate and optimize resources for effective deployment. Technology plays a crucial role in decision-making processes, enhancing real-time responses to threats and opportunities.
Product Design and Delivery
Product design and delivery involve collaboration between marketing, design, production, engineering, and materials teams. Operations management provides manufacturing design, cost insights, and supply chain optimization. It oversees quality assurance, logistics, and distribution to ensure timely delivery of products and services.
Process Optimization
Process optimization is crucial for efficient use of resources and elimination of bottlenecks. Operations managers analyze and enhance processes using flowcharting, mapping, and simulation techniques. By identifying inefficiencies and implementing improvements, they streamline operations and overcome challenges like space shortages or inventory management.
Daily Target Achievement
Operations management plays a crucial role in supporting the achievement of daily targets. It ensures efficient resource utilization, process optimization, and focus on key performance indicators (KPIs). Automation, real-time tracking, and communication tools enhance efficiency and address operational issues promptly.
Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Purchasing and supply chain management involve coordinating activities to ensure the smooth flow of materials, timely deliveries, and cost-effective operations. Operations management aligns strategic goals with procurement and supply chain activities. It builds relationships with purchasing and cost control teams, optimizing supply chain practices.
Project Planning and Control
Operations management provides frameworks and oversight for efficient project planning and control. It collaborates with project managers to develop realistic timelines, assess risks, and allocate resources. Project planning and control enable efficient execution, risk management, and successful project outcomes.
Scheduling and Task Management

Operations management plays a crucial role in scheduling and task management. It breaks down projects into activities, milestones, and deliverables. By creating visual process maps, operations managers ensure clear task assignments and effective time management. Task scheduling platforms enhance collaboration, progress tracking, and workflow efficiency.
Material and Equipment Management
Material and equipment management involves optimizing resource utilization, inventory management, and supply chain efficiency. It balances material availability, lowers costs, and enhances customer satisfaction. Material requirements planning (MRP) ensures timely production and procurement of materials.
Capacity Management
Operations management ensures organizations have the right resources to meet current and future demand efficiently. It balances production capabilities with market demand, optimizing resource utilization and output. Capacity management ensures timely delivery, quality standards, and high productivity.
Productivity Management
Effective productivity management ensures optimal use of labor, capital, and outputs. It enhances communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills. Operations management identifies weaknesses and strengths, uses project management tools, and provides rewards and feedback to boost productivity.
Essential Skills You Need to Succeed as an Operations Manager

To succeed as an operations manager, several essential skills are required:
Analytics
Operations managers analyze and interpret data to track business functions and make informed decisions. They must develop knowledge of data computing platforms and leverage business insights to optimize operations.
Risk Analysis
Operations managers perform risk analysis to identify potential risks and develop solutions. They analyze risks related to data security, talent management, and changing regulatory environments.
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning aligns organizational goals with departmental objectives. Operations managers integrate finance, HR, accounting, and marketing into strategy management. They analyze economic and industry data to provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Decision-Making
Operations managers make decisions at various levels, from policy-making to process control and quality management. They analyze options, allocate resources, and ensure efficient decision-making.
Budget Management
Budget management is crucial for cost control and financial planning. Operations managers prepare operating budgets and adhere to ethical standards when handling financial information. They use budgeting and accounting software to streamline processes.
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a crucial skill for operations managers. They analyze challenges, identify solutions, and implement improvements. They create standard operating procedures to define goals and objectives and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Communication
Effective communication is essential for managing relationships with stakeholders. Operations managers use clear and concise expression, active listening, and empathy to enhance communication. They leverage technology and nonverbal cues for effective communication.
Leadership
Effective leadership contributes to organizational success. Operations managers develop interpersonal skills, strategic thinking, and commitment to personal and team growth. They mentor and inspire their teams to achieve goals.
Organization
Operations managers prioritize tasks efficiently, maintain clear systems, and set realistic goals. They utilize tools and technologies to streamline workflows, enhance time management, and create an organized work environment.
Product Development
Product development skills are valuable for operations managers. They oversee the product lifecycle, collaborate with cross-functional teams, and ensure product quality and timely delivery. Product development skills help create innovative and customer-centric products.
How SweetProcess Can Make Your Job Easier as an Operations Manager

SweetProcess is a powerful tool that can streamline your operations management tasks. It provides process documentation and collaboration features to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Map Out and Document Your Company’s Procedures and Processes using SweetProcess
SweetProcess allows you to easily create and document processes for your organization:
- Log in to your SweetProcess account.
- Use the Add Teams feature to select teams you want to share processes with.
- Use the Procedures and Policies tab to look up or create processes.
- Choose a process and add it to your account.
- SweetProcess AI can generate a process in minutes. Alternatively, manually create your process using the easy-to-use interface.
How to Collaborate With Team Members in Real-Time Using SweetProcess
SweetProcess enables real-time collaboration with team members:
- Create and assign roles to new teams.
- Add members to roles and assign them teammate or super manager status.
- Team members can comment and respond to comments via the SweetProcess interface or email.
How to Track and Monitor the Progress of Tasks Assigned to Team Members in SweetProcess
SweetProcess includes task management features to track and monitor progress:
- Assign tasks to team members using the three-dots menu or the “Actions” menu.
- Create one-off or repetitive tasks and assign them to individuals or teams.
- Ensure all team members complete their tasks using SweetProcess’s tracking features.
SweetProcess is a valuable tool for managing your operations effectively, enhancing collaboration, and improving productivity.
Types of Operations Management
Objectives Management

Objectives management monitors the implementation of company strategy and evaluates deviations. It aligns goals with strategy, monitors external and internal forces, and adjusts plans accordingly.
Task Management
Task management oversees intermediate processes and ensures alignment with objectives. It focuses on internal data pipelines, corrective actions, and process optimization.
Individual Supervision
Individual supervision ensures that overall strategy is met through ground-level supervision. It oversees individual efforts, communicates instructions, and mitigates risks in real-time.
Major Performance Objectives of Operations Management
Quality
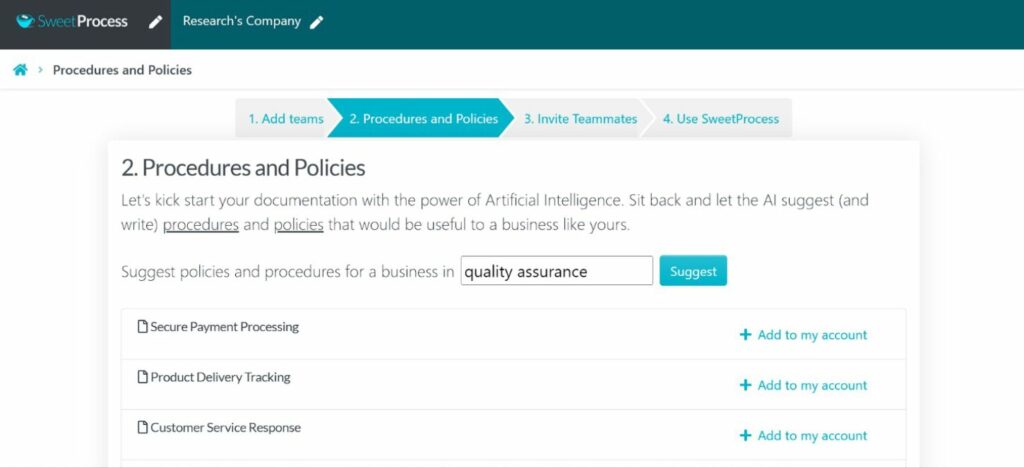
Quality is a consistent indicator of integrity, performance, and customer satisfaction. Operations management focuses on achieving and maintaining high-quality standards to lower costs and improve customer satisfaction.
Speed
Speed is essential for meeting customer expectations and minimizing inefficiencies. Fast turnarounds save costs, reduce inventory, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Dependability
Dependability ensures that promises are made and kept. Operations management focuses on meeting customer needs, enhancing responsiveness, and maintaining consistent quality standards.
Cost
Operations management aims to lower costs through efficient resource utilization, elimination of non-value-added activities, and optimization of processes. Cost reduction leads to lower prices and increased sales.
Flexibility
Flexibility is crucial for rapidly responding to threats and opportunities. Operations management embraces technology, decentralizes decision-making, and fosters a culture of adaptability.
Frameworks for Analyzing Operations Management
Value Chain
Value chain analysis identifies the customer’s source of value and opportunities for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It examines the entire sequence of activities involved in creating and delivering a product or service.
System Thinking
Systems thinking analyzes the dynamics, conditions, and restraints of a process. It examines the interconnectedness of system parts and identifies behavior patterns for process improvement.
Business Process Reengineering
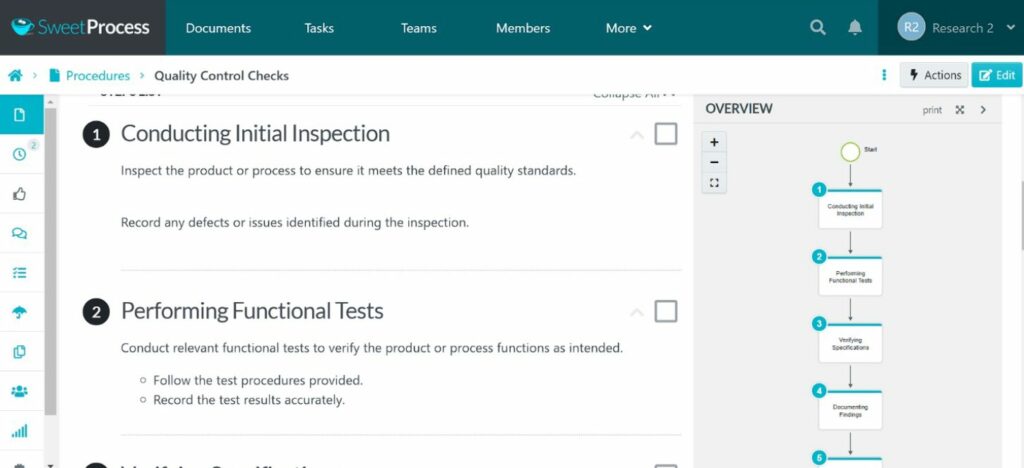
Business process reengineering involves radical redesign and improvement of existing processes. It enhances efficiency, streamlines workflows, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Critical Path Analysis
Critical path analysis identifies the most time-consuming project sequence that must be completed before the project can be considered finished. It helps plan project schedules and manage dependencies effectively.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing minimizes waste, optimizes processes, and maximizes efficiency. It focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities, reducing inventory, and enhancing overall productivity.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma analyzes processes to identify and eliminate defects or variations. It uses statistical methods to improve quality, reduce errors, and increase efficiency.
Challenges of Operations Management (And How to Overcome Them)
Safety
Maintaining a safety culture is crucial for operations management. Communicating safety processes, providing training, and fostering a safety-conscious environment are essential for mitigating workplace hazards.
Global Operations
Global operations present challenges in terms of cultural differences, regulatory environments, and logistical intricacies. Operations managers must adapt to diverse business environments, leverage technology for efficient communication, and navigate complex supply chains.
Quality Control
Ensuring consistent quality is a challenge in many businesses. Operations managers must emphasize the importance of quality control, provide support and resources, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Process Improvement
Process improvement is essential for maintaining excellence. Operations managers must identify areas for improvement, implement efficient technologies, and foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.
Labor Shortage
Talent shortage is a growing challenge for operations management. Operations managers should reimagine their hiring processes, upskill their teams, embrace diversity, and collaborate with educators to develop talent pipelines.
Time Management
Effective time management is crucial for meeting deadlines and minimizing delays. Operations managers should prioritize tasks, automate processes, and implement efficient scheduling systems to enhance time management.
Advanced Technology Adoption and Integration
Adopting and integrating advanced technology can be challenging due to initial costs, resistance to change, and compatibility issues. Operations managers should research and select technologies with easy learning curves, involve team members in the decision-making process, and anticipate security vulnerabilities.
Sustainability
Sustainability challenges arise from a lack of transparency, changing consumer preferences, and rising upfront costs. Operations managers should implement eco-friendly practices, reduce waste, and comply with environmental regulations. Integrating sustainability into the business model ensures long-term resilience.
Factors Influencing the Performance of Operations Management
Type of Organization (Service or Product-Based)
The type of organization, including its size, industry, and market orientation, directly impacts operations management. Different organizations have unique strategies, processes, and priorities that guide their operations.
Volume
Volume impacts operations management, with higher volumes requiring streamlined processes, automation, and efficient supply chain management. Large-scale operations focus on scalability and cost-effectiveness, while lower volumes prioritize flexibility and responsiveness to market changes.
Variation (In Demand)
Demand variability can lead to delays and stockouts. Operations management must be adaptable to handle fluctuations and optimize resource utilization during peak demand while minimizing inefficiencies during lulls.
Variety
A wide variety of products or services may require flexible production systems and diverse skill sets. Operations management balances customization with efficiency to meet customer demands for varied offerings.
Customer Contact
The level of customer contact influences operations management. High customer contact requires a focus on customer experience, responsiveness, and flexibility. Low customer contact emphasizes efficiency, standardization, and cost-effectiveness.
Manage Your Business Operations Effectively Using SweetProcess
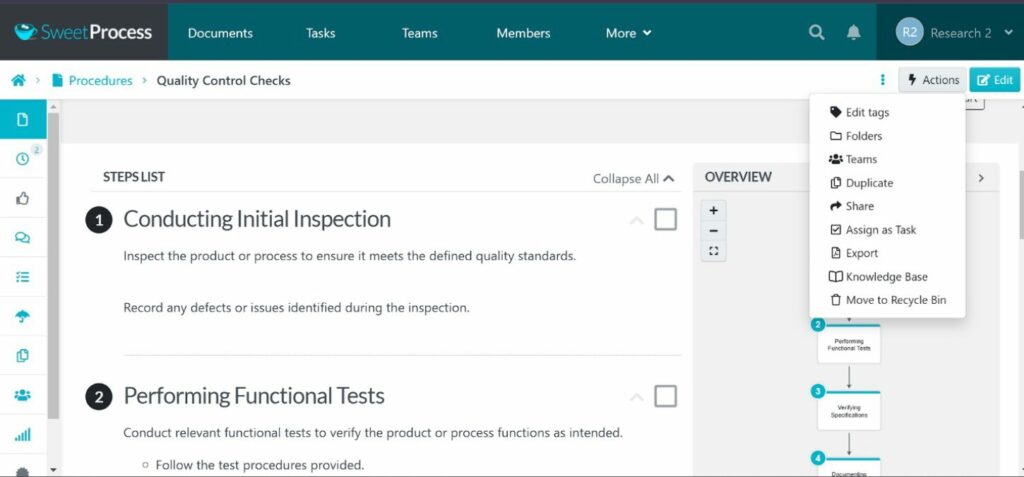
SweetProcess is a powerful tool that can help you streamline your business operations effectively. It provides process documentation, task management, and collaboration features to enhance efficiency, productivity, and overall performance.
Sign up for a free 14-day trial of SweetProcess and experience how it can revolutionize your operations management. With its intuitive interface and powerful features, SweetProcess is the tool you need to succeed in today’s competitive business environment.
Remember, effective operations management is key to creating value for customers, shareholders, and the entire business ecosystem. Embrace the power to act and optimize your operations using SweetProcess.
